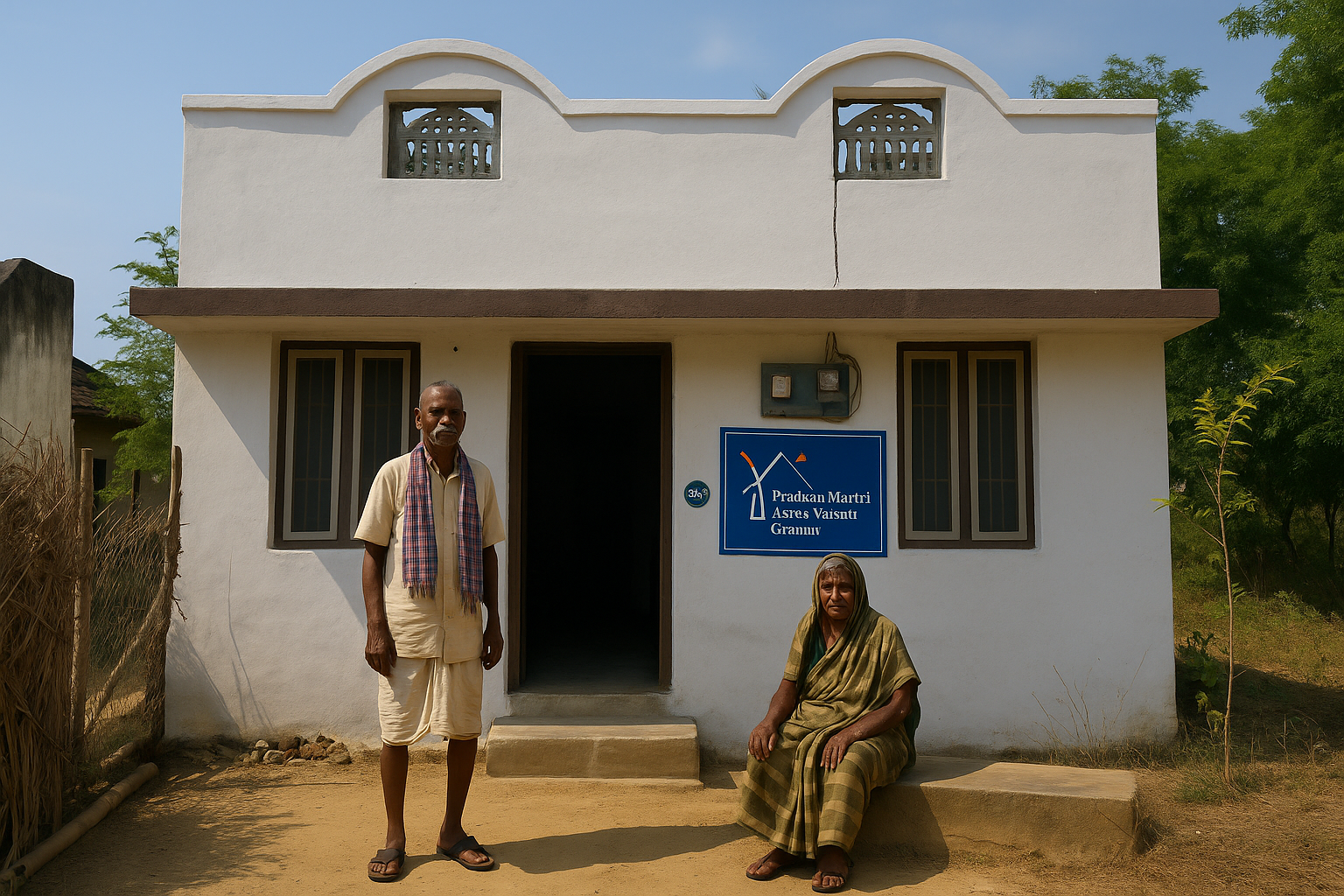
Under the Indian Government initiative of “Housing for All”, Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Gramin (PMAY-G) has emerged to empower rural people with a pucca house with basic amenities. This scheme is dedicated to those people who live in a kuchcha house or have no home in a rural area.
Keep reading further, as this article touches upon every important aspect of the PMAY rural scheme with updated numbers and facts. So, keep a keen eye throughout this article to gain the benefit of this productive scheme offered by the Indian Government.
PMAY-G Scheme Highlights — Updated 2025
| Particulars | Details |
| Purpose of the Scheme | To provide rural people who live in a kuchcha house or have no home in a rural area with a pucca house equipped with basic amenities. |
| Launched by | Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD), Indian Government |
| Implemented by | Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) |
| PMAY-G Scheme (Original) Approval Date | 23rd March 2015 (by the Union Cabinet) |
| Implementation Date | 1st April 2016 |
| Official Launch / Inauguration Date | 20th November 2016 |
| PMAY-G scheme (Original) 1st Period | 2016 – 2019 (extended to March 2024) |
| PMAY-G scheme 2nd Period | 2024 – 2029 (till March 2029) |
| PMAY-G scheme 2.0 Approval Date | 9th August 2024 (by the Union Cabinet) |
| Target of houses to be built in the PMAY-G scheme (2016 – 2024) | 2.95 crore |
| Target of houses to be built in the PMAY-G scheme (2024 – 2029) | An additional 2 crore |
| Financial Assistance in the PMAY-G scheme | Rs 1.20 lakh in plain areas Rs 1.30 lakh in hilly/extreme areas Additional financial support through convergence with schemes like Swachh Bharat Mission, MGNREGA, Saubhagya, Jal Jeevan Mission, Ujjwala Yojana, and NRLM |
General Overview of PMAY-G
The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Rural (original) was launched and implemented as a more structured form of the Indira Awas Yojana (IAY) under the tagline “Housing For All” in rural areas. This scheme caters to rural people who live in kutcha or dilapidated houses in rural areas.
Under this scheme (2016 – 2024), 2.95 crore houses were supposed to be completed by March 2024. However, by April 2025, 2.75 crore houses have been completed. This scheme extends to March 2029 (2024 – 2029) to build an additional 2 crore houses in rural areas.
For FY 2024-29, the total amount planned or earmarked is Rs 3,06,137 crore, and for FY 2024-25, the total amount allocated is Rs 54,500 crore. With these additional two crore houses, approximately ten crore individuals are expected to benefit.
To ensure smooth implementation, various independent institutes, like NITI (National Institute for Transforming India) Aayog, National Institute of Public Finance and Policy, Panchayati Raj, and National Institute of Rural Development, etc, evaluate this Pradhan Mantri Rural Awas Yojana.
Notable Features and Benefits Under the PMAY-G Scheme
The Gramin Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana is equipped with multiple features and benefits, providing rural people with a full-fledged pucca house in a streamlined manner. The following table clearly depicts the features and benefits of this scheme:
| Features / Benefits | Details |
| House Size | Provides a house size of a minimum of 25 square meters, with a dedicated kitchen space. |
| Financial Assistance | Rs 1,20,000 per unit in plain areas; Rs 1,30,000 per unit in hilly, difficult, and IAP districts |
| Financial Support through multiple Convergences | Convergence with Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM-G): Up to Rs 12,000 for toilet construction Convergence with MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act): Beneficiaries get 95 days of work as unskilled labor at Rs 90.95 per day with Rural Mason Training during construction. Convergence with Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY): One LPG connection per house |
| Basic Amenities | With various government programs, beneficiaries of this scheme get a pucca house equipped with an electricity connection, clean cooking fuel, waste treatment, insurance coverage, and piped drinking water. |
| Loan Facility | Beneficiaries may have the option to opt for a home loan of up to Rs 70,000 at a lower interest rate of 3% to expand or upgrade their home. |
| Subsidy | Beneficiaries may get an interest subsidy of 3% on loans up to Rs 2,00,000 principal. |
| Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) | As a beneficiary of the PMAY-G scheme, you get your payments directly to your Aadhaar-linked bank/post office account. |
| Beneficiary Identification | Beneficiaries’ selection for this scheme depends on various factors like Geo-Tagging, Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC 2011) Awaas+ (2018) surveys, and Gram Sabha approvals. |
| House Design | Beneficiaries are free to choose suitable designs as per their specific region. |
| Self-survey and Field-level surveyors | The PMAY-G scheme features a self-survey process via the Awaas + 2024 mobile app, where beneficiaries can know about their eligibility through Aadhaar-based face authentication for this scheme. When facing failure in performing a self-survey process, beneficiaries can complete their survey with the help of field-level surveyors. These surveyors are appointed by the government authorities to assist households while self-registering. |
| Female Homeownership Empowerment | With 74% (as of writing) of houses sanctioned for female ownership (solely or jointly), the scheme demonstrates its emphasis on women’s homeownership empowerment. |
| Employment Generation | By providing training to almost 3 lakh rural masons in disaster-resilient construction, Pradhan Mantri Gramin Awas Yojana is boosting employment for local people. |
| Sustainable Construction | The scheme emphasizes the use of eco-friendly and locally available sustainable building materials and techniques to promote environmentally friendly home construction. |
Current Progress in PMAY-G – Latest Statistics and Information
As per the government source (as of writing), the total number of registered houses is around 3.93 crore. Out of the registered 3.93 registered houses, around 3.78 crore houses have been sanctioned, and approximately 2.78 crore houses have been completed in this scheme. This paves the way for a total of funds transferred 3,77,853.97 Cr.
As per another government source, the target allocated by the ministry during 2024-25 is 84,37,139 to 18 states. In December 2024 and January 2025, 46,56,765 houses have already been allocated to the 9 states. As of 2nd February 2025, 39,82,764 houses have been sanctioned out of the targeted (84,37,139) figures.
This progress is making a dramatic shift in the rural housing scenario, by reducing poverty, fostering social and economic development, and enhancing living standards in rural India.
Eligibility Criteria for PMAY-G
The eligibility criteria under the PMAY-G scheme are a bit complicated to understand, as they depend on various factors. You need to have enough understanding of those factors to cope with this while applying for this scheme.
That’s why we mention a table below that incorporates a dedicated section for all the related factors to the Gramin Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana eligibility criteria:
| Factor | Description |
| Basic Eligibility | Beneficiaries are selected based on the Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) 2011, further verified by Gram Sabhas. Rural People who don’t have any shelter. Households that depend on alms or live in extreme poverty. Manual Scavengers. Primitive Tribal Groups. Legally released bonded laborers. |
| Prioritization Framework | Households categorized as Scheduled Castes (SC)/Scheduled Tribes (ST), minorities, and others are prioritized for this scheme. Rural people who are houseless, or have one-room or two-room houses with kutcha walls and roofs, are prioritized respectively. Households with fewer rooms or no homes get prioritization over households with more rooms within each social category. |
| Special Consideration for Compulsory Inclusion | Rural People with the following features automatically fall under the higher priority group: Households featuring no adult members between the ages of 16 to 59. A rural family without any literate adults over 25 years of age. Households headed by women and lacking an adult male between the ages of 16 and 59. Households without land rely heavily on manual work as a source of income. Households with no healthy adult and any disabled member. |
| Target Earmarkings | For SC/ST: 60% of the targets are reserved for SC/STs for each state or UT, as per the eligibility. For Minorities: As per the rural population (based on the latest census) of Minorities, 15% of the funds are reserved for minorities at the national level. For Persons With Disabilities (PWDs): The PMAY-G scheme may ensure that 5% of beneficiaries at the State Level are from among Persons with Disabilities under the provisions of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act of 2016. For Households Affected by Natural Disasters: An additional 5% of the target is reserved for households affected by natural disasters, such as Cyclone Fani in Odisha. |
| Tie-Breaking Criteria | In case of a tie within a subgroup, prioritization is executed as per the following: A rural family with a single girl child is prioritized. Households with widows or surviving family members of law enforcement, military, or defense personnel killed in combat. Cancer, leprosy, and HIV affected members of a rural family. Household beneficiaries under the Forest Rights Act, 2006. |
Exclusion Criteria
Households featuring the following criteria are automatically excluded from this scheme:
- Households use the Kisan Credit Card, which features a credit limit of Rs 50,000 or above.
- Households with Government jobs or non-agricultural enterprises.
- Households that pay income/professional tax or earn a monthly salary of above Rs 15,000.
- Households owning assets, such as irrigated land of more than 2.5 acres, landline phones, and refrigerators.
Important Things to Remember
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Gramin is a beneficial scheme for underprivileged rural people, fulfilling their most basic needs of living in a pucca house equipped with basic amenities. However, this scheme may become complicated for beneficiaries if they don’t understand its intricacies.
This section is dedicated to those important things about this scheme that are worth remembering:
- All processes involved in this scheme are online, featuring functionality such as Awaas App and Awaas Soft.
- At each construction stage, every house gets geo-tagged.
- For direct fund transfers, the scheme uses platforms like e-FMS and PFMS.
- The scheme emphasizes the quality and timeliness of home construction completion.
- In every Gram Panchayat, there is a provision for conducting a social audit at least once a year.
- To assess the progress of the scheme, the officers of the ministry and National-Level monitors visit PMAY-G houses during the field visits, selecting beneficiaries for the scheme.
- The Performance Index Dashboard tracks various scheme implementation factors, which assist with the planning of necessary interventions in required areas.
- Beneficiaries must participate in a self-survey via the Awaas + 2024 app or be surveyed by a government official to apply for PMAY-G online. E-KYC is necessary to complete the self-survey.
- State governments are in charge of tracking progress and submitting Annual Action Plans.
- For identification and fund disbursement, Aadhaar and face authentication are mandatory under the PMAY-G scheme.
- Upon house completion and verification, the final installment will be released.
Beneficiaries or the Public can lodge complaints on the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS) portal (pgportal.gov.in) to resolve their issue. Additionally, mechanisms like IGRS and the CM helpline at the State Level are beneficial for the same.